The specialists at CASA DENTALIS Oral Surgery treat numerous diseases of the teeth, jaws and oral cavity every day. Here we explain some of the outpatient operations and available applications of oral surgery.
Outpatient surgeries
Here, the patient can be discharged home on the same day of the procedure. Thanks to state-of-the-art anesthesia procedures, medical technologies and surgical techniques in oral surgery, outpatient surgery can be performed more and more frequently.Implantology
Implantology is a highly advanced, complex dental field of work and usually requires additional specialized training. The insertion of dental implants is painless under local anesthesia and is performed in an outpatient surgery.
The surgical removal of wisdom teeth
- if they lead to or have already led to pathological changes in the jaw (e.g. abscesses due to slipped angle infections) or in neighboring teeth (e.g. resorptions of the tooth root)
- when wisdom teeth do not develop properly
- When wisdom teeth are deeply destroyed by caries or have inflammation at the root tip
- when wisdom teeth interfere with the clenching of the teeth
- Wound infections
- Post-bleeding
- Temporary or, very rarely, permanent damage to nerves in the lower jaw that supply sensation to the lower teeth, tongue, and lip.
- Risk of jaw fracture 4 weeks after surgical removal of wisdom teeth
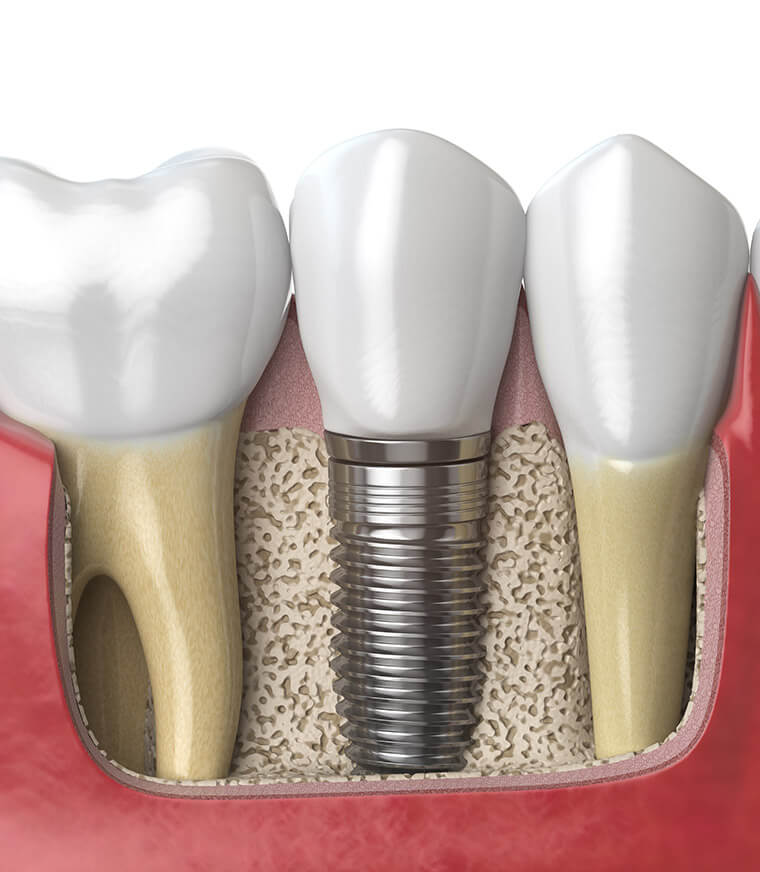
By means of a surgical procedure, usually under local anesthesia, an implant is inserted into the jawbone like a kind of “artificial tooth root”.
Implants are useful when:
- own, completely healthy teeth should not be ground or so that existing crowns or special fillings (e.g. made of ceramics) do not have to be removed;
- Due to the size of the tooth gap or its location/type (shortened row of teeth), only removable dentures would be possible.;
- removable dentures or total prostheses cause very serious functional problems.
- Implantation is a surgical procedure; it is usually performed on an outpatient basis (without hospitalization) and is performed under local anesthesia (without anesthesia).
- Depending on the implantation site and bone quality, implants heal in three to six months, with healing taking place faster in the mandible than in the maxilla.
- During the healing period, a (temporary) denture is usually worn over the implants. After healing, which with most implant systems takes place “invisibly” for the patient under the mucosa, the implant(s) must be exposed in a second operation. The implant(s) must be uncovered in a second operation so that the impression and the fabrication and insertion of the denture can take place at this time or a few days later.
- With regard to the risks associated with implantation, in the mandible, attention must be drawn above all to possible injury to the nerve running in the bone (trigeminal nerve).
- If damaged or even severed, there is a partial or complete numbness (similar to that experienced after anesthetic injection) in the lower lip/chin area where the nerve damage occurred.
- Implant placement in the maxilla may result in damage/penetration of the surgical drill and implant into the nasal or maxillary sinus floor.
- After completion of the healing phase, the “artificial root” is followed by the further restoration with the denture.
- For this purpose, an abutment is inserted into the artificial tooth root and the planned denture is fabricated in several working steps.
- After completion of the tooth replacement treatment, it is necessary to have a regular check-up by the dentist. He will check the condition of the implant as well as the oral hygiene situation and give advice on care.
- The use of special cleaning aids, such as interdental brushes and/or dental floss, ensures that the implant remains in place for a long time and prevents inflammatory bone resorption processes (implantitis).
- Depending on the individual risk, professional dental cleanings are necessary.
- Despite all the advances in implantology, this is a tooth replacement and not an alternative to natural teeth. The own, natural and healthy tooth is and remains the best restoration.
- Yes, in addition to good oral hygiene usual for oral health, special aids and techniques for cleaning dentures and implants should be used in addition to the normal toothbrush, depending on the type of restoration. For example Bridges should be cleaned daily on their underside with a special dental floss with a fluffy cleaning component. Implants should also be cleaned with such a floss or with special interdental space brushes.
- The patient should be instructed in the necessary hygiene measures by his dental practitioner or by appropriately trained specialists (dental prophylaxis assistant). It is also advisable to have a checkup performed at regular intervals – at least every six months.
- A wealth of studies are available on the success evaluation of bridge and implant restorations. It has been shown that implants usually heal without problems. Long-term problems are more likely to arise in connection with general oral health. Diseases of the periodontium, such as periodontitis, can also occur on implants (periimplantitis).
- Implant loss is often related to inadequate oral hygiene, especially after prolonged implant wear, but often it is also due to individual factors (smoking) or changes in the general health of the patient. health of the patient that can lead to implant loss. It is important that optimal oral hygiene is possible around the implant in any case.
- In addition to the correct indication, planning and implementation of a dental prosthesis or implant restoration, good oral hygiene and care of the prosthesis are important prerequisites for its long-term success in otherwise healthy patients who do not belong to a risk group.
An apicoectomy is a surgical procedure in which the inflamed root tip of a tooth is capped, the inflamed area is removed, and the inside of the tooth is cleaned. This form of treatment is an attempt to preserve the tooth.
- The decision to perform an apicoectomy is up to your Casa Dentalis dentist and will be discussed in detail during a consultation.
- Wound infections
- Post-bleeding
- Damage to adjacent teeth
- temporary or very rarely occurring damage to nerve structures in the lower jaw that provide sensation to the lips, tongue and lower teeth
- Irritation or inflammation of the maxillary sinus in the upper jaw
In the case of teeth that, despite carefully performed Periodontal treatment
progressive bone loss and high pocket depths, a surgical procedure is often necessary.
often require a surgical procedure.
Frenulum correction (frenectomy):
Correction or removal of the labial frenulum is necessary when the fibrous strand is so thick and tight that it results in a permanent gap between the central incisors. In this case, the frenulum is removed in a minor surgical procedure under local anesthesia. frenulum is removed. The optimal time for frenectomy is between the ages of 8 and 9.Tongue frenulum correction:
If the lingual frenulum is shortened, tongue mobility is restricted. This can cause problems in infants with breastfeeding, drinking, swallowing and, later on, difficulties with speech development. The correction of a shortened lingual frenulum is performed under local anesthesia in a small surgical procedure by incision or laser and usually does not require suturing.Bone augmentation (jaw bone augmentation) is the reconstruction of lost bone substance in the jaw.